What is a J-1 Visa? The J-1 Visa 2025 is a non-immigrant visa that allows international students, scholars, interns, and professionals to participate in cultural and educational exchange programs in the United States.
This visa enables participants to gain hands-on experience through research, academic study, or professional training under designated U.S. sponsors, promoting cross-cultural understanding and global collaboration.
Unlike traditional student visas, the J-1 focuses on practical learning, cultural immersion, and international networking, making it perfect for anyone seeking a meaningful global experience.
This guide covers J-1 Visa eligibility, application steps, program categories, and essential requirements to help you confidently plan your U.S. exchange journey.
J-1 Visa Overview
The J-1 visa operates as a structured cultural exchange program with specific requirements and benefits:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Visa Type | Nonimmigrant Cultural Exchange (J-1) |
| Sponsor Required | Yes, must be a U.S. Department of State-designated sponsor |
| Duration | 3 weeks to 7 years (varies by category) |
| Work Allowed | Limited – only if authorised by the sponsor |
| Dependents | J-2 visa for spouse/children |
| Path to Green Card | Not directly; may require waiver or change of status |
| DS-2019 Required | Yes, Certificate of Eligibility for Exchange Visitor Status |
The J-1 visa requires sponsor approval and offers limited work authorization, with program duration varying significantly based on the specific exchange category and participant objectives.
What is the J-1 Visa Exchange Visitor Program?
The J-1 Exchange Visitor Program, operating under the BridgeUSA initiative, was established through the Mutual Educational and Cultural Exchange Act of 1961.
This program strengthens international relationships through educational and cultural collaboration between the United States and participating countries.

The program includes several categories: interns, professors, research scholars, students, au pairs, and teachers.
Each category helps promote cross-cultural understanding and professional growth.
J-1 Visa Eligibility Requirements
To qualify for a J-1 visa, applicants must meet several essential criteria:
- Program Acceptance: Gain acceptance into a program sponsored by a designated U.S. host organisation, such as a university or approved institution.
- Funding Requirements: Secure funding from non-personal sources, including government grants, institutional awards, or organisational sponsorship.
- Financial Documentation: Demonstrate adequate financial resources to cover living expenses, tuition, and program costs throughout the stay.
- Academic/Professional Standards: Meet specific academic qualifications, training requirements, or professional criteria corresponding to your designated J-1 category.
- English Proficiency: Possess sufficient English language skills to successfully participate in the chosen program and communicate effectively.
J-1 Visa Application Documents Checklist
Essential documents required for a J-1 visa application include:
- Valid Passport: Your passport must remain valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay in the United States.
- DS-2019 Form: Certificate of Eligibility for Exchange Visitor Status, properly signed and reviewed by your sponsor.
- Financial Support Documentation: Bank statements, scholarship award letters, or funding confirmation from sponsors.
- SEVIS Fee Receipt: Proof of payment for the Student and Exchange Visitor Information System fee.
- DS-160 Confirmation: Completed Online Nonimmigrant Visa Application with confirmation page.
- University Admission Letter: Official acceptance documentation if participating in academic programs.
- Visa Photograph: Recent photo meeting U.S. Embassy specifications and requirements.
- Application Fee Receipt: Proof of payment for non-immigrant visa processing fees.
- Supporting Documents: Academic transcripts, English proficiency test scores, and evidence of ties to the home country
J-1 Visa Program Fees
Program fees vary among sponsor organisations based on exchange categories, program duration, and specific requirements.

Most sponsors charge participants directly, unless they are participating in federally funded programs.
1. SEVIS Fee:
The mandatory SEVIS I-901 fee (approximately $220) supports the Student and Exchange Visitor Information System.
Some sponsors pay this fee on behalf of participants, while others require individual payment. Participants receive payment confirmation receipts, which are required for visa interviews and other official purposes.
2. Visa Application Fees:
Each J-1 applicant is required to pay non-immigrant visa processing fees at a U.S. embassy or consulate.
Government-sponsored participants with DS-2019 forms displaying G-1, G-2, G-3, or G-7 program serial numbers are exempt from these fees.
3. Visa Issuance Fees:
Additional reciprocity fees may apply based on bilateral agreements between the U.S. and the applicant’s home country.
Government-sponsored exchange visitors and dependents are typically free from both application and issuance fees.
J-1 Visa Categories
The J-1 visa program has different exchange visitor categories. Each one crafts specific academic, professional, and cultural exchange goals. This helps meet the varied needs of international participants.
| Category | Purpose |
|---|---|
| College/University Student | Enrolled in a U.S. academic program on an exchange terms |
| Short-Term Scholar | Brief academic or research engagements (up to 6 months) |
| Research Scholar/Professor | Long-term academic collaboration or research (up to 5 years) |
| Intern | Structured internship tied to the field of study (12 months) |
| Trainee | Professional training beyond academics (18 months max) |
| Au Pair | Live-in child care with educational requirement (12–24 months) |
| Teacher | Qualified teachers in U.S. schools (3 years, renewable) |
| Camp Counselor | Summer camp work & culture exchange |
| Specialist | Individuals with specialised knowledge or skills (1 year) |
| Physician | Graduate medical education (requires special approval) |
Below, we explore the most common categories and what they include
College/University Student
Students enrolled in accredited U.S. academic institutions participate in structured exchange programs.
These programs emphasise cross-cultural learning and academic collaboration between American and international educational systems, typically lasting one academic year with possible extensions.
Short-Term Scholar
Academic professionals engage in brief research projects, consultations, or scholarly activities lasting up to six months.
This category accommodates visiting faculty, researchers, and specialists conducting focused academic work without long-term commitments.
Research Scholar/Professor
Long-term academic collaborations allow scholars and professors to conduct extensive research or teach at U.S. institutions for up to five years.
Participants contribute to academic advancement while gaining international research experience and professional development.
Intern
Students and recent graduates participate in structured internship programs directly related to their field of study.
These programs offer valuable hands-on experience, helping to bridge academic knowledge with real-world applications.
These 12-month programs provide practical work experience, professional skill development, and cultural immersion in American workplace environments.
Trainee
Professionals with relevant work experience receive specialised training in their field for up to 18 months.
Trainees gain exposure to advanced techniques and industry standards to enhance their career prospects internationally.
Programs focus on advanced skill development, industry best practices, and professional networking beyond basic academic learning.
Au Pair
Young adults provide live-in childcare for American families while pursuing educational requirements.
This experience fosters personal growth through cultural exchange, language immersion, and building lifelong connections.
Programs last 12-24 months and emphasise cultural exchange, language learning, and childcare experience in American family settings.
Teacher
Qualified educators teach in U.S. primary or secondary schools for up to three years with renewal possibilities.
This opportunity promotes educational diversity and helps broaden student perspectives through international teaching styles.
Programs address teacher shortages while providing American students with exposure to international teaching perspectives and methodologies.
Camp Counselor
International students work at summer camps, providing recreational activities and cultural exchange opportunities.
Counsellors develop leadership skills while creating memorable experiences for youth from diverse backgrounds.
These seasonal programs typically last 3-4 months and emphasise youth development and cross-cultural understanding.
Specialist
Individuals with specialised knowledge, skills, or expertise share their talents with American organisations for up to one year.
This exchange encourages professional growth and the transfer of unique expertise across industries.
This category accommodates unique professional exchanges that don’t fit other J-1 categories.
Physician
International medical graduates participate in graduate medical education programs requiring special approval and extensive documentation.
These physicians receive advanced clinical training to meet U.S. healthcare standards while contributing to medical research and patient care.
These programs address healthcare workforce needs while providing advanced medical training opportunities.
How to Request A DS-2019 Form For J-1 Visa?
Contact your program sponsor or university admissions office to initiate the DS-2019 request process.
Upon meeting the eligibility requirements, sponsors provide detailed instructions for completing and submitting the form.
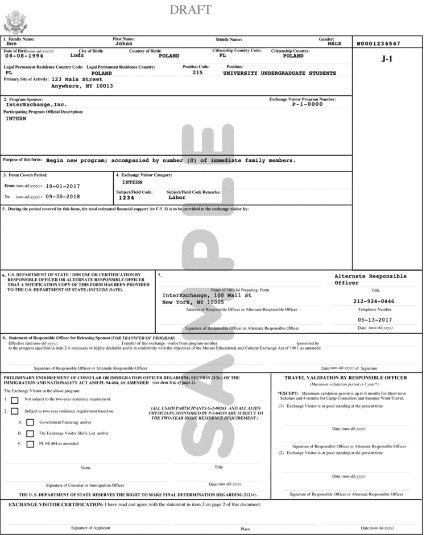
Ensure all supporting documentation, including financial statements, passport information, and funding verification, remains current and accurate.
Universities typically distribute DS-2019 request links through their international student offices, while other sponsors may have specific application portals for prospective participants.
How To Apply For J-1 Visa: Step-By-Step Process
Follow these steps to apply for a J-1 visa through a sponsor program successfully.
Step 1: To apply for a J-1 visa, find a sponsor from the U.S. State Department’s list. They may require English proficiency and assist with your application.

Step 2: Receive your DS-2019 Certificate of Eligibility from your program sponsor after meeting all program requirements and providing necessary documentation.
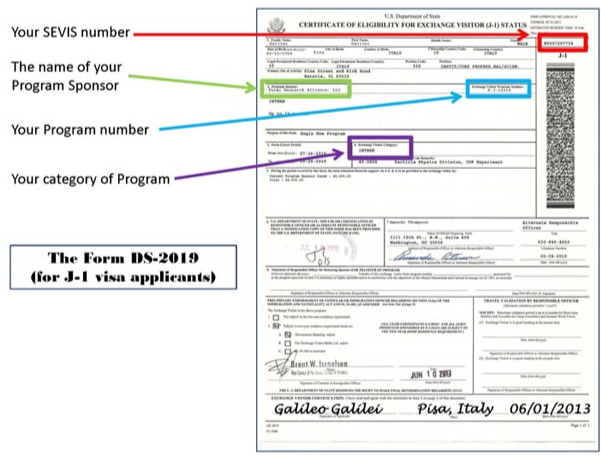
Step 3: Pay the mandatory SEVIS I-901 fee through the official Department of Homeland Security website and retain the payment receipt for your records.
Step 4: Complete the DS-160 Online Nonimmigrant Visa Application form accurately and submit it through the official U.S. State Department website.
Step 5: Schedule your visa interview appointment at the U.S. embassy or consulate in your home country through their official appointment system.
Step 6: Attend your visa interview with all required documents, including your passport, DS-2019 form, financial evidence, SEVIS receipt, a recent photograph, and fee payment confirmations.
Step 7: Await the consular officer’s decision and receive your visa stamp if approved, then prepare for travel to the United States.
Receiving a DS-2019 form does not guarantee visa approval. Consular officers assess your ties to your home country, financial support, and intent to return after the program.
Online Presence and Social Media Review in J-1 Visa Applications
Beginning in 2025, all F-1 and J-1 visa applicants will be required to provide social media account information on their DS-160 applications.
Applicants should ensure their social media profiles are publicly accessible during the application review process.
Consular officers screen accounts for potential security concerns, inappropriate content, or information contradicting visa application details.
Maintaining a professional online presence and avoiding content that may be considered controversial helps ensure a smooth visa processing and approval.
Admission to the U.S. on a J-1 Visa
J-1 visa holders may enter the United States up to 30 days before their program start date indicated on the DS-2019 form.
Upon arrival at the port of entry, present your valid passport, DS-2019 certificate, and visa stamp to Customs and Border Protection officers.
Officials will issue an I-94 arrival record stamped with “D/S” (Duration of Status), indicating authorised stay length.
Maintain all original documents throughout your program, as they may be required for travel, employment authorisation, or program compliance verification.
J-1 Visa and Two-Year Home Residency Requirement (212e)
Certain J-1 participants face the two-year home residency requirement under Section 212(e) of the Immigration and Nationality Act.
This requirement applies when participants receive government funding, possess skills on the U.S. Exchange Visitor Skills List, or participate under formal international agreements.
Individuals affected by this requirement must return to their home country for a period of two years before applying for an H, L, K, or immigrant visa.
Waivers may be available through government recommendations, interested government agency requests, or persecution claims.
Advisory opinion services help determine 212(e) applicability when status remains unclear.
J-1 vs F-1 vs H-1B Visa Comparison
Understanding the key differences between the J-1 and F-1 visas, and how they compare to other types of visas like the H-1B, can help you choose the right option for your educational, cultural exchange, or work goals.
| Aspect | J-1 Visa | F-1 Visa | H-1B Visa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cultural exchange and practical training | Academic study and research | Employment in a specialty occupation |
| Funding | Often requires institutional or government sponsorship | Typically self-funded or private scholarships | Employer-sponsored; no personal funding requirement |
| Work Authorization | Limited work through sponsor approval | Optional Practical Training (OPT) and Curricular Practical Training (CPT) | Full-time work allowed with sponsoring employer; no OPT/CPT required |
| Restrictions | May include a two-year home residency requirement | Generally, fewer post-graduation restrictions | Tied to employer; changing jobs requires filing a new H-1B petition |
| Duration | Varies by program (usually 6 months – 7 years) | Duration of academic program plus optional OPT | Initially up to 3 years, extendable to 6 years |
| Family | Can bring spouse/children on J-2 visa (with limited work authorization for spouse) | Can bring spouse/children on F-2 visa (spouse cannot work) | Can bring spouse/children on H-4 visa (spouse may work if H-1B holder has approved I-140) |
The F-1 visa focuses on academic pursuits and student self-funding, whereas the J-1 visa includes broader cultural exchange, including work training, and typically requires institutional sponsorship.
In contrast, investor-focused options such as the UAE Golden Visa target long-term residency.
J-1 participants may face additional restrictions like the 212(e) requirement, but often gain more diverse practical experience and cultural immersion opportunities.
The H-1B visa is designed for skilled professionals to work in specialty occupations in the U.S., sponsored by an employer. Unlike J-1 or F-1 visas, it focuses on employment rather than study or cultural exchange.
J-1 Visa For Citizens of Canada or Bermuda
Canadian and Bermudian citizens enjoy streamlined J-1 visa procedures without requiring traditional visa stamps.
However, DS-2019 certificates and SEVIS fee payments remain mandatory requirements.

These citizens present all required documentation directly at U.S. ports of entry, similar to some cases where travel is permitted without a passport, provided there are no prior embassy interviews.
Border officials process J-1 applications at entry points, making the process more convenient while maintaining program integrity and security requirements.
J-1 Visa Eligibility (2025 Criteria)
To qualify for a J-1 Exchange Visitor Visa in 2025, applicants must meet specific program-based criteria and demonstrate a genuine purpose aligned with cultural exchange, education, or professional training in the United States.
Eligibility varies by category, but the visa is primarily open to the following program types:
- Students (High School & University Programs)
- Researchers & Scholars
- Interns & Trainees
- Teachers & Professors
- Physicians (Medical Training Programs)
- Au Pairs & Camp Counselors
- Short-Term Specialists & Visiting Professionals
- Summer Work-Travel Participants
Under the updated policy framework, applicants must also be officially sponsored by a U.S. Department of State-approved exchange program. Sponsorship is now more strictly enforced to ensure programs meet academic or professional development objectives, rather than personal travel or work interests.
Also Read:
Conclusion: Empowering International Visitors Through the J-1 Exchange Program
The J-1 Visa 2025 enables international students, interns, researchers, and professionals to participate in U.S. cultural and educational exchange programs, fostering global collaboration and cross-cultural understanding.
By engaging in research projects, internships, teaching exchanges, or professional training, participants gain practical skills, career development opportunities, and invaluable international experience. These programs not only enhance the visitor’s growth but also contribute to the enrichment of U.S. institutions and communities.
With careful preparation and awareness of J-1 visa requirements, this program offers a transformative path to academic, professional, and cultural advancement in the United States.
FAQs
The J-1 visa enables international students, scholars, and professionals to participate in U.S.-based cultural exchange programs sponsored by organisations, promoting mutual understanding between nations.
Employment is permitted only when explicitly authorised by your program sponsor and must directly relate to your program objectives and educational or training goals.
SEVIS (Student and Exchange Visitor Information System) is a government database that tracks J-1 exchange visitors and their dependents throughout their stay in the United States.
The SEVIS I-901 fee is approximately $220, which supports the monitoring system and must be paid before your visa interview, with a payment receipt required for application processing.
Your spouse and unmarried children under 21 years old can apply for J-2 dependent visas to accompany you during your authorised stay in the United States.



